Aspertaan (Aspartame) Explained : The Truth Behind This Popular Sweetener

Clarifying The Name: “Aspertaan”
You may sometimes see the term “Aspertaan” mentioned in articles, discussions, or product labels. It’s important to note that this is likely a misspelling or mispronunciation of “Aspartame”, the well-known low-calorie artificial sweetener.
All scientific research, official labeling, and regulatory approvals refer to Aspartame, not “Aspertaan.” Any benefits, risks, or uses attributed to “Aspartame” should be understood as relating to it. Including this clarification in your content ensures readers understand the correct terminology and avoids confusion.
What Is Aspertaan?
Aspertaan is a calorie-reduced artificial sweetener commonly used in place of sugar in diet and sugar-free foods. Chemically, it’s made from two amino acids — phenylalanine and aspartic acid — bonded together with a small methyl group. Because humans don’t metabolize it like sugar, it provides sweetness with very few calories.
Aspartame is approximately 200 times sweeter than regular sugar, which means only a tiny amount is needed to achieve the desired sweetness. That’s why it’s popular in products where reducing calorie intake is a priority.
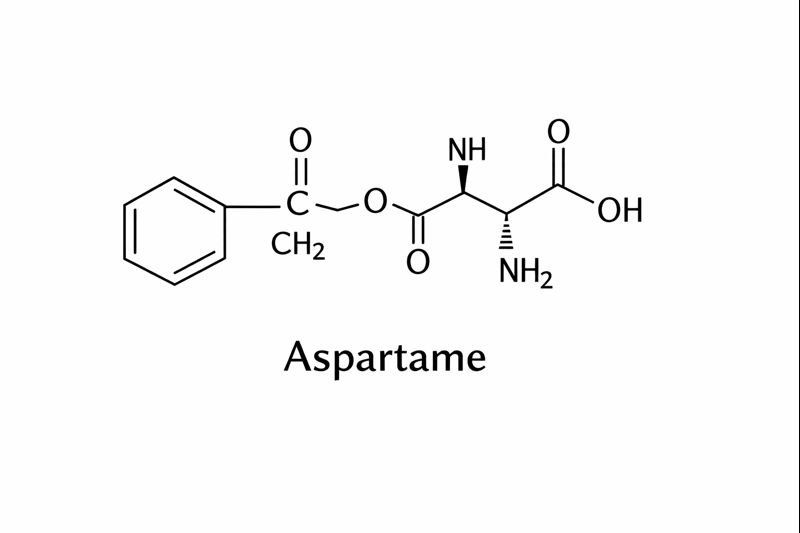
Molecular Structure and Chemical Formula of Aspertaan (Aspartame)
The molecular formula of aspartame (often misspelled as aspertaan) is:
C₁₄H₁₈N₂O₅
Aspartame is a dipeptide compound, meaning it is formed by linking two amino acids: aspartic acid and phenylalanine, along with a methyl ester group. This unique structure is responsible for its intense sweetness, which is significantly stronger than regular sugar.
At the molecular level, the structure allows aspartame to interact strongly with sweet taste receptors on the tongue, even in very small amounts. Because of this, only minimal quantities are needed to achieve sweetness, resulting in a low-calorie profile.
When consumed, the molecule breaks down into its natural components during digestion, which is why its structure is closely studied in nutritional and metabolic research.
How Aspertaan Works
When you consume Aspartame, your digestive system breaks it down into its components: phenylalanine, aspartic acid, and methanol. These components are naturally found in many foods, and at the small amounts produced, they are typically considered safe for most people.
Although it tastes sweet, aspartame doesn’t spike blood glucose levels like sugar does. This makes it useful for people managing weight or blood sugar levels.
Common Uses of Aspertaan
Aspertaan appears in a wide range of foods and beverages, including:
Diet sodas and energy drinks
Sugar‑free gum
Low‑calorie desserts and puddings
Reduced‑sugar tabletop sweeteners (packets)
Sugar‑free dairy products
Some medicines and chewable vitamins
Manufacturers often choose aspartame because it delivers sweetness without adding calories, and it mixes well in liquids and soft foods.
Benefits of Aspertaan
Aspartame offers several advantages, especially for people seeking calorie control:
1. Helps Reduce Calorie Intake
Replacing sugar with aspartame can significantly cut calories, which may support weight management efforts.
2. No Effect on Blood Glucose
Unlike table sugar, aspartame doesn’t raise blood sugar levels, making it popular with people who have diabetes.
3. High Sweetness, Small Amount Needed
Because it’s about 200 times sweeter than sugar, only a tiny amount is required for the same sweetness level.
4. Versatile Ingredient
Aspartame works well in a variety of products, from drinks to chewing gum, without affecting taste quality.
Potential Disadvantages and Safety Concerns
Although approved by health authorities globally, aspartame has been the subject of debate. Some potential drawbacks include:
Phenylketonuria (PKU) Risk
Individuals diagnosed with phenylketonuria (PKU), a rare inherited condition, should not consume aspartame. People with this condition cannot break down phenylalanine, which is present in Aspertaan.
Controversial Health Claims
Aspartame has been linked in some studies to headaches, mood changes, and digestive issues. However, many of these associations are not conclusively proven.
Not Suitable for High‑Heat Use
Aspartame breaks down at high temperatures, so it’s not recommended for baking or cooking at high heat.
Aspertaan vs. Sugar: What’s the Difference?
Aspertaan and sugar differ in several key ways:
Calories:
Sugar contains about 4 calories per gram.
Aspartame contributes almost no calories due to its intense sweetness.
Blood Sugar Impact:
Sugar can raise blood glucose levels.
Aspartame does not affect blood glucose.
Taste:
Sugar offers a familiar taste but adds bulk.
Aspartame is much sweeter and used in tiny amounts.
While sugar is a natural carbohydrate, aspartame is a synthetic sweetener. Both have pros and cons depending on individual health goals and preferences.
Safety and Regulatory Approval
Aspartame has been extensively studied for decades. Big health organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and those in the United States, Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have reviewed research and approved it for general use within recommended limits. The acceptable daily intake (ADI) for aspartame is set based on body weight, and most people consume much less than this limit even with daily use of diet beverages or sweeteners.
Despite ongoing public debate, regulatory agencies continue to consider aspartame safe for the general population, with the exception of individuals with PKU.
Who Should Avoid Aspertaan?
The only group that must avoid Aspertaan is people with PKU (phenylketonuria), a rare genetic condition affecting how the body processes phenylalanine. For someone with PKU, phenylalanine can build up and cause harmful effects, so all products containing aspartame must be labeled to warn these individuals.
Tips for Using Aspertaan Wisely
If you choose to include aspartame in your diet, here are a few tips:
Use it in products that help you reduce overall calorie intake.
Check labels carefully, especially if you have PKU.
Avoid using aspartame in recipes requiring high heat.
Balance its use with whole, unprocessed foods.
FAQs About Aspertaan
Q1. Is aspartame safe for children?
In approved amounts, it is considered safe for children, except those with PKU.
Q2. Does it cause cancer?
There is no conclusive evidence that aspartame causes cancer when consumed within recommended limits.
Q3. Can diabetics use it?
Yes, since it does not raise blood sugar levels.
Q4. How much it can I eat per day?
The acceptable daily intake is based on body weight and generally well above what most people consume.
Q5. Is aspartame natural or artificial?
It is an artificial sweetener developed to mimic sugar’s sweetness without calories.
Conclusion
Aspertaan remains one of the most commonly used artificial sweeteners in the world. It offers a way to reduce calorie and sugar intake while enjoying sweetness in beverages and food. Although debates about its effects continue, scientific evidence supports its safety when consumed within recommended guidelines. Whether you’re managing weight, blood sugar, or simply looking for sugar alternatives, understanding aspartame can help you make informed dietary choices.